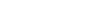Biotechnology is the exploitation of biological processes for the development of technologies and products for a specific use.
GlobalData’s Strategic Intelligence report on biotech details how recent developments of certain technologies are impacting the industry.
AI, cloud computing, and data analytics help the analysis of complex biological data, which advances what biotech can achieve. For example, machine learning can look at complex data sets and identify potential patterns and predict biological functions. Gene editing tools like CRISPR enable precise modification of DNA. These technologies are revolutionary. For example, they can treat genetic diseases and create disease-resistant crops.
Elsewhere, synthetic biology can create new biological systems that enable the construction of new products like biofuels or therapeutics. Advancements in synthetic biology will improve the production of textile materials, enabling customisable properties (for example, color) and sustainable production.
Biotechnology and fabrics
Industrial biotechnology uses biotechnology tools to design and engineer sustainable materials from renewable resources. The aim is to make products and materials that are efficient, adaptable, and sustainable. Biotechnology-based developments will have a significant impact on several industries, particularly those trying to reduce their emissions.
The apparel industry accounts for 10% of greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, companies are working on new materials that are developed from bio-sources, including wood-based fabrics, bio-engineered spider silks, and seaweed-based fabrics.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe biotechs pioneering new textiles
For example, Viscose is the third most popular textile in the world, and Rubi Laboratories (a San Francisco-based start-up) converts carbon dioxide from textile manufacturing facilities into viscose with plant enzymes. Rubi’s material is water-neutral, carbon-negative, and naturally biodegradable.
Seaweed is being used to create bio-based fabric. For example, Keel Labs (a North Carolina-based start-up) utilises seaweed to create fabric that uses 70 times less water than cotton and does not use pesticides. The cotton industry spends between $2bn and $3bn on pesticides annually, according to Keel Labs.
Big brands are partnering with biotech to create sustainable materials. For example, Lululemon launched its first product using plant-based nylon in April 2023, partnering with biotech company Genomatica to use a biotech process to convert plant sugars into nylon. This product is a sustainable and recyclable alternative to traditional materials.
A growing number of brands are using these next-generation materials. Runway shows in New York, London, and Paris in spring and summer 2025 included an array of innovative fabrics.